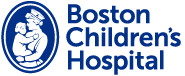Quicklinks
Interested in using the CIC? Prerequisite: Training is required for all investigators prior to first time usage of any specific equipment in our facility.
Please fill out a Service Request Form (see above).
Cellular Imaging Gallery
Optic nerve crush leads to induced phosphorylation of cyclic AMP in retinal cells.
Section of the mouse retina showing some of the localization of pCREB (red) in Muller cells labeled with muller cell marker CRALBP (green). DAPI stains the nuclei (blue).
Hui-ya Gilbert, Benowitz lab
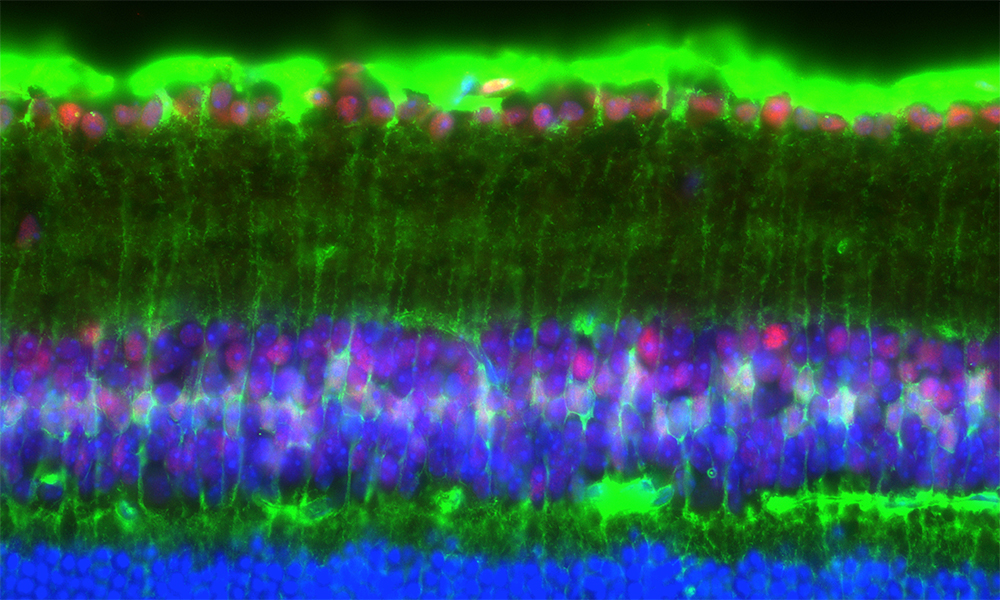
Tau seeding assay in HEK293T cells
Cells stably expressing mutant Tau-EYFP were treated with pathological Tau seeds to induce Tau aggregations, which is an important pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease brain (shown), whereas cells treated with control do not show aggregations (not shown).
L. Chen, Steen lab
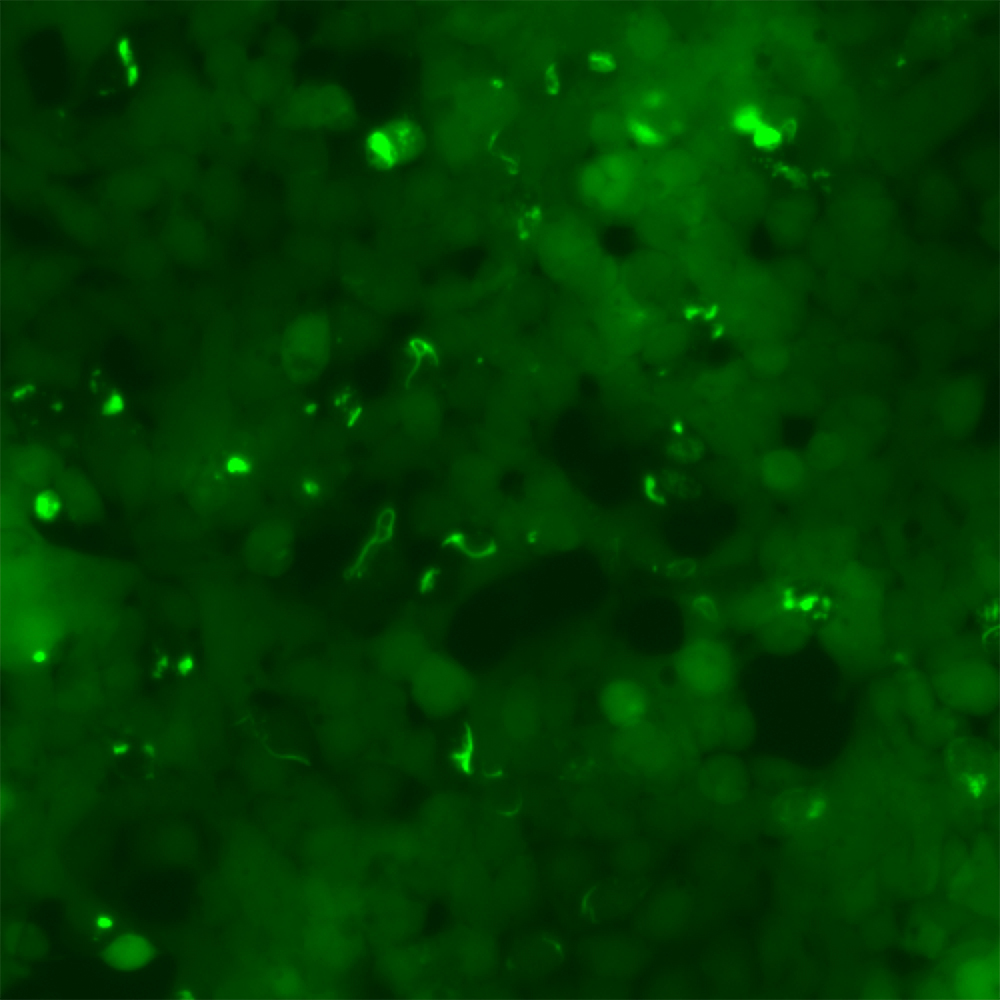
Macrophage & Dextran imaging
CX3CR1-GFP expressing macrophages
Imaging paradigm: 20min baseline recording of Choroid Plexus tissue through a cannula window (about 3.5-4mm below bregma).
Shipley and Dani et al., 2020
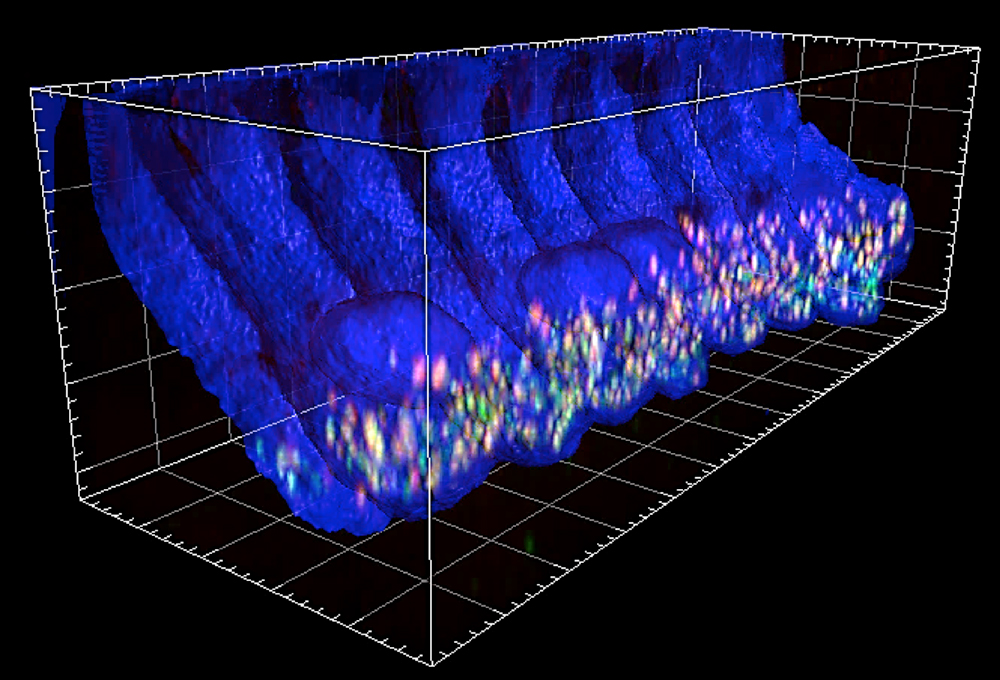
Cochlea from WT, Tmc1/2 single and double KO mice were harvested at various timepoints from P7 to P28.
Each cochlea was microdissected and immunostained for CtBP2 to label ribbons, GluA2 to label the postsynaptic afferent contacts, and Myo7a to label hair cells. Frequency maps were generated using apex-to-base length measurements. Confocal z-stacks of the 8.0, 11.3, 16.0, 22.6, and 32.0kHz regions were obtained and image stacks were ported to Imaris, an image analysis software where 3-D projections were generated and the average number of synapses per inner hair cell were counted.
J. Lee, Holt-Geloc Lab

Megakaryocyte tethers and neutrophil entry into a CD41+ vacuole.
MKs stained with anti-CD41 (green) were co-cultured with marrow cells from mT/mG mice (red) in the presence of Draq5 (DNA, blue). Image shows a neutrophil on the MK surface, attached by MK tethers.
Cunin et al., 2019